Introduction
Capabilities are one of the most misunderstood concepts in modern businesses. The idea isn't new, you only have to look at how the defence and nuclear industry have used this term for over 20+ years. Quite often people use the terms capabilities and function interchangeably, but it's important to note that they are NOT the same thing and can NOT be used in this interchangeable manner. In this section of the TOGAF AIDES Space, we attempt to define capability and demonstrate why it's not just a function.
Capability can be defined as - the ability to achieve a desired effect in a specific operating environment, it is a logical construct that is made manifest through the components of an organisation.
Conepts
Capabilities are high level building blocks that can be arranged in a number of ways to allow an enterprise to achieve it's goals. Let's try and resolve the mystery surrounding this term.
Consider a situation where you are looking to employ the services of a builder to do some work on your home. What key characteristics would you consider when you're looking to employ someone in this role?
- skills (physical competency - bricklaying, plumbing, electrical work, roofing, carpentry etc)
- competencies (education, qualifications and areas of knowledge - bricklaying, plumbing, electrical work, roofing, carpentry etc)
- cost
- work ethic (turns up on time, is diligent and doesn't leave a job half done, honesty
- how quickly they get the job done - can they deliver in the time allotted
- customer relationship management (how much they keep me informed about the costs and what they are doing) - communications skills
- tools (good knowledge of the right tools for the job) - equipment
- quality (consider TQM as defined by Toyota)
- how well organised are they, this will involve the team around them and how effectively they work as a team
Use the following statement as a guide to this thinking "being able to do building work doesn't make you a competent builder". Most people can run (to some degree), this doesn't make them competent runners, that competency comes from training, eating well and plenty of sleep. In other words there are number of key characteristics that must be developed in order to enable that capability.
The next thing to remember about a capability is that it is more than just a business function, service or team. It is a logical entity with distinct measurable characteristics (described above) that work together to achieve a goal. Typically a capability considers the following (a MOD perspective on the characteristics of a capability (TEPIDOIL)
- skills and competency (roles/personnel)
- training
- philosophy (way of thinking)
- equipment (operational level)
- organisation (required organisation structure)
- information (data and processes)
- infrastructure (platforms, communications, and core primary services)
- logistics (pulling it all together)
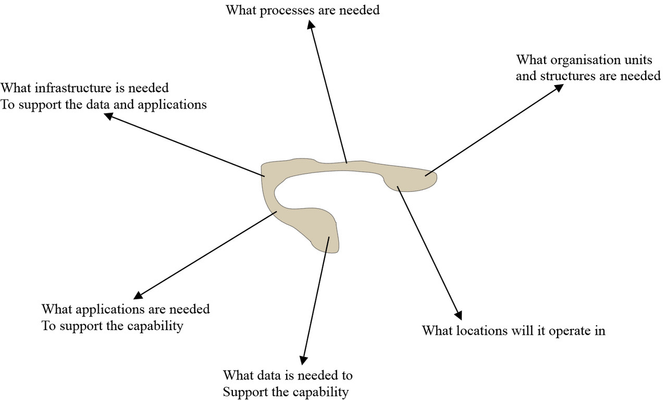
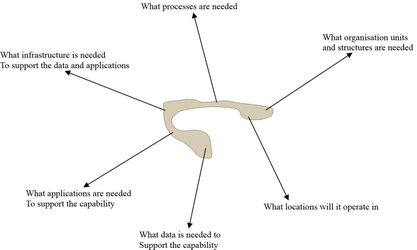
Alternatively one could choose to define capability from the architectural unification approach POLDAT
- Process (business processes)
- Organisation (structures)
- Location (Geographical information)
- Data (models, life cycles, security etc)
- Application (software, security, interoperability etc)
- Technology (infrastructure)
Both TEPIDOIL and POLDAT pay no attention to organisation unit boundaries (business unit, sector, service, function etc) but weave a path through organisation units, selecting those areas within those units that, deliver the characteristics needed by the capabilities.
More often than not, a goal is delivered through multiple capabilities
We can now start to see that as we weave through the different parts of the organisation we need to ask the following questions (to help define the nature and characteristics of a capability)
The nature of a capability
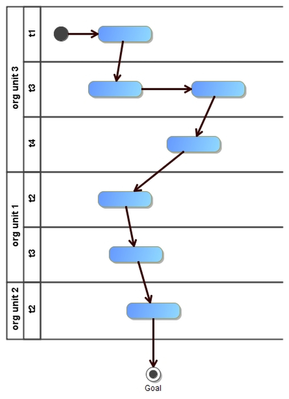
Our next task is to try and illustrate this weaving nature that we have described above? One approach that we are currently trying is to map the thread through a UML activity model. We use swimlanes to provide a visual way of representing organisational units and other sub units.
This model captures the weaving nature through our first example of one capability to deliver a goal |
|---|
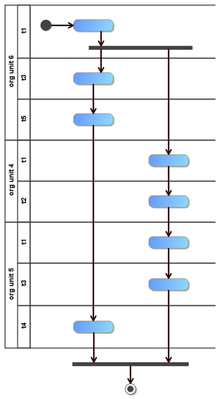
In this example we show multiple capability paths delivering a goal |
|---|
So how does this help me
That's a very good question and it depends on your perspective; there are several that I would like to describe and I am sure that you can think of others.
Partnership to deliver a goal(s)
in this context the partners will have some clearly defined goals but, they similar even the same set of capabilities which makes it easier to do like for like comparison allowing you to ignore the physical implementation e.g. comparing the check-in or baggage handling capabilities across airports. These partners will clearly want to know which of them has the best capability to help deliver the goal(s).
Comparison strategy
If within an industry sector a clear set of capabilities have been defined, it becomes easier to compare companies within that sector without getting bogged down in the implementation detail (business functions, services, software and hardware etc).
Industry alignment
You want to compete in a particular sector but the way in which you are structured and operate doesn't allow you do a like for like comparison with your competitors. So you take an industry defined capability model, look at its goals and determine how would you align your organisation up against the industry standard to bring about those capabilities to deliver those goals.
Creating new goals/opportunities
Once you have gone through the exercise of defining your capabilities which when combined in certain ways deliver certain goals, it now becomes possible to combine those capabilities in other ways to discover what other goals can be achieved, in other words what opportunities do the new combinations create.
Tactical alignment to strategic goals
Your defined capabilities are there to deliver a long term strategy. In the interim, pressure points force you to respond to them through short term goals. These short term goals require certain adjustments to your long term defined capabilities, the capability increments (up or down) result in work being down in your organisation to handle the pressure point. The aim is to not change the long term strategy (capabilities) but adjust them to deliver the short and long term goals.
Defining a capability
Defining a capability is an extensive task but once done can lead to a major simplification in the overall understanding and modelling of a enterprise.
Start by asking the following questions
Consider the following example, you you want to build a home from scratch, core required capabilities
- architecture
- building services (described above)
- garden landscaping
- land (with planning permission) - a key resource !